1:进入RAM控制台,创建一个RAM用户 访问方式一般选择OPenApi就可以了
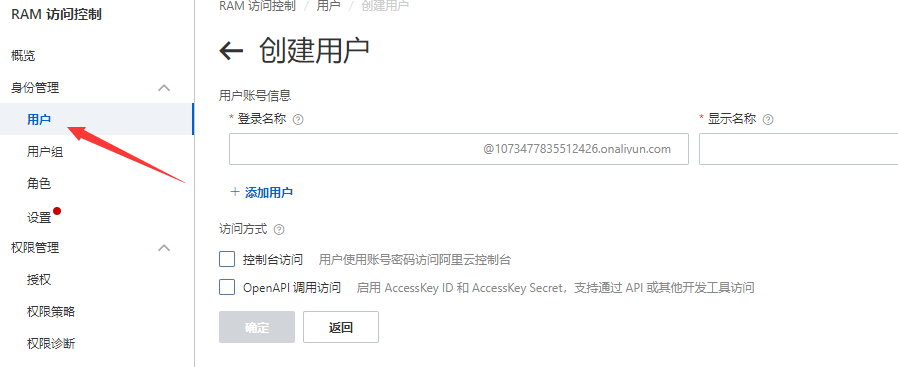
登陆名称自己随意填写不重复就可以,确定后添加成功
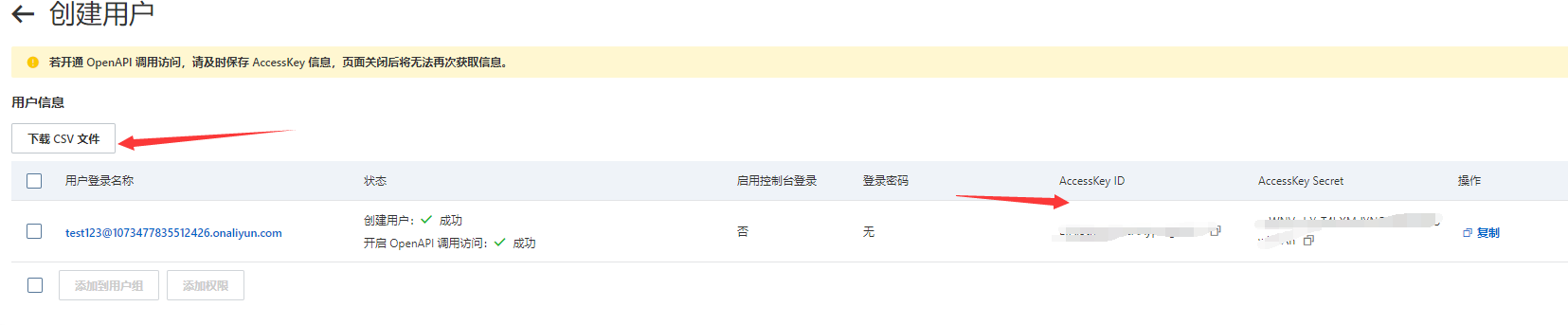 生成的密钥信息可以保存到本地。
生成的密钥信息可以保存到本地。
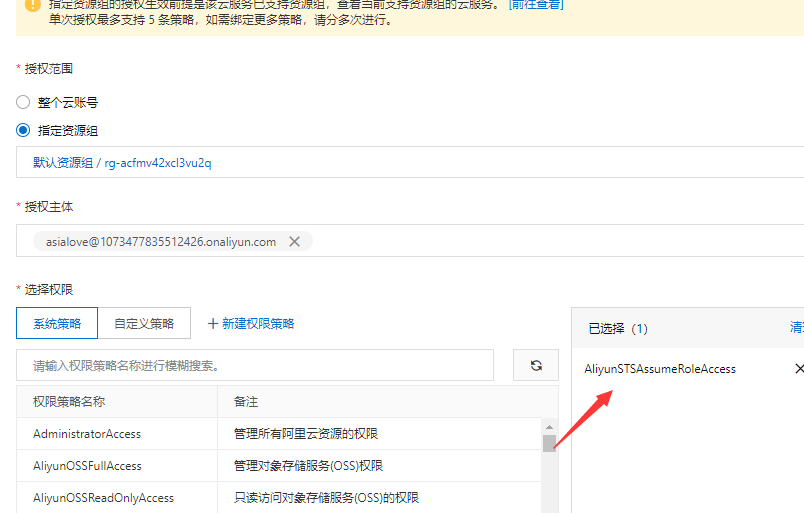
2:为RAM用户添加系统策略
添加AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess权限 这个步骤主要创建了一个用于获取临时访问凭证的角色,获得角色ARN
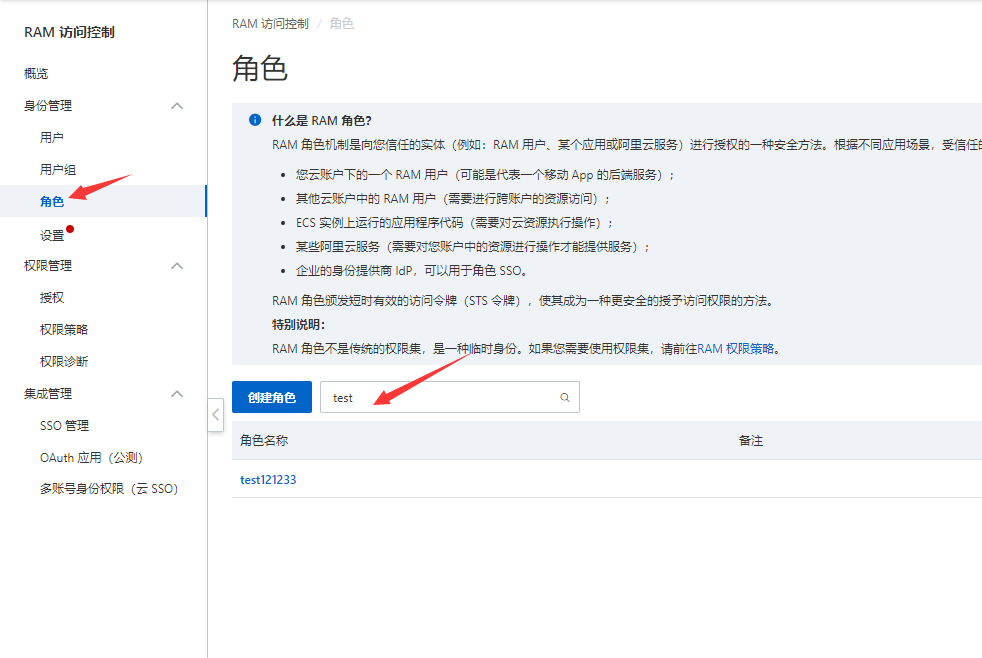
3:创建角色
如图:选择角色-> 创建角色
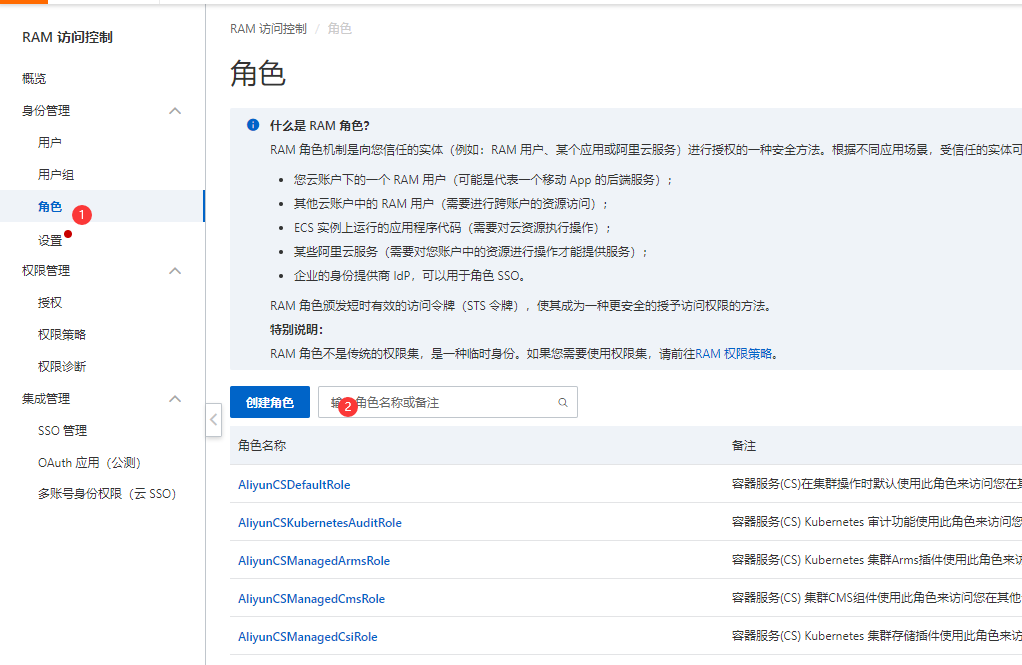
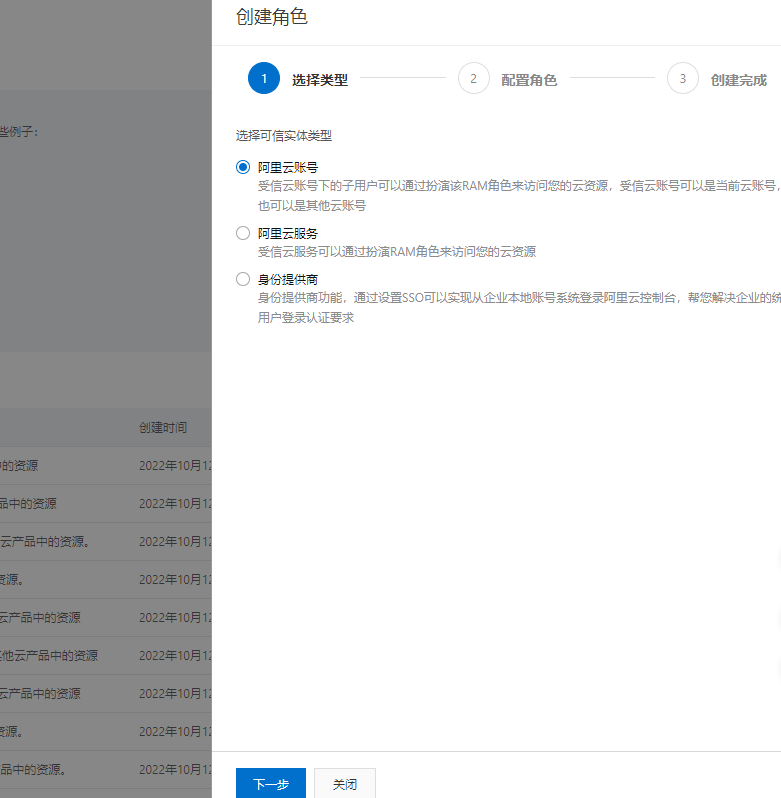
类型选择阿里云账户
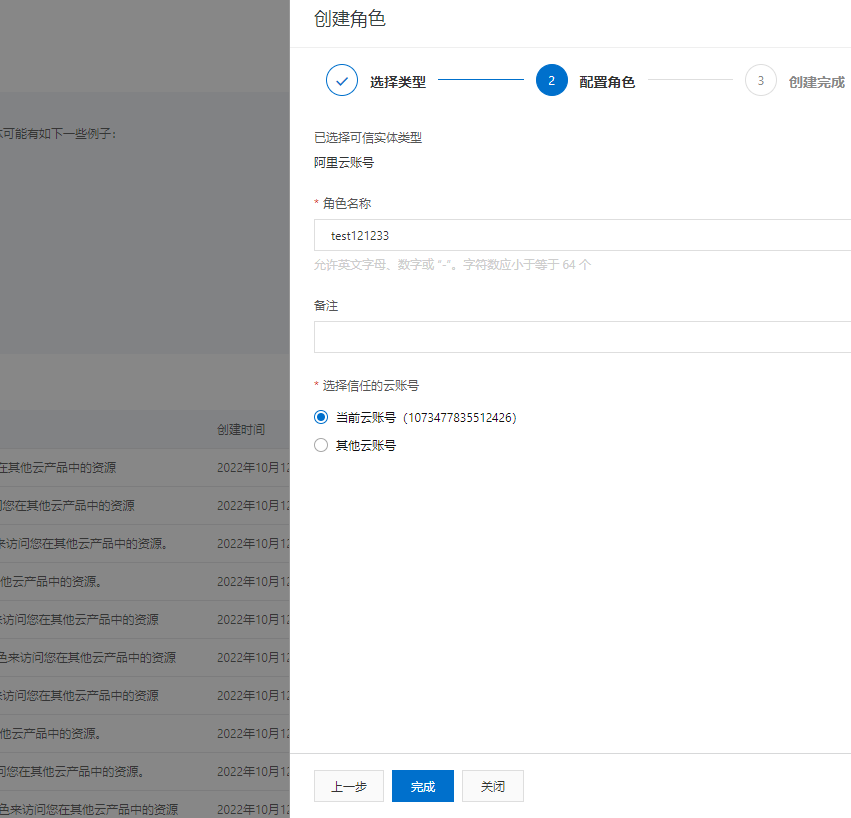
添加角色名创建完成
这里的角色名称和ARN保存一下后续代码中要用到
4:创建策略
这里主要通过自定义策略实现,选择左边权限管理-》权限策略-》创建策略
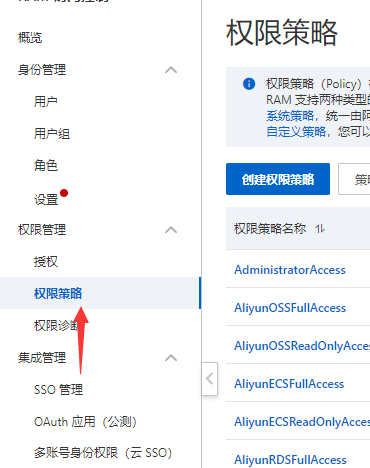
切换到脚本编辑模式填写脚本内容
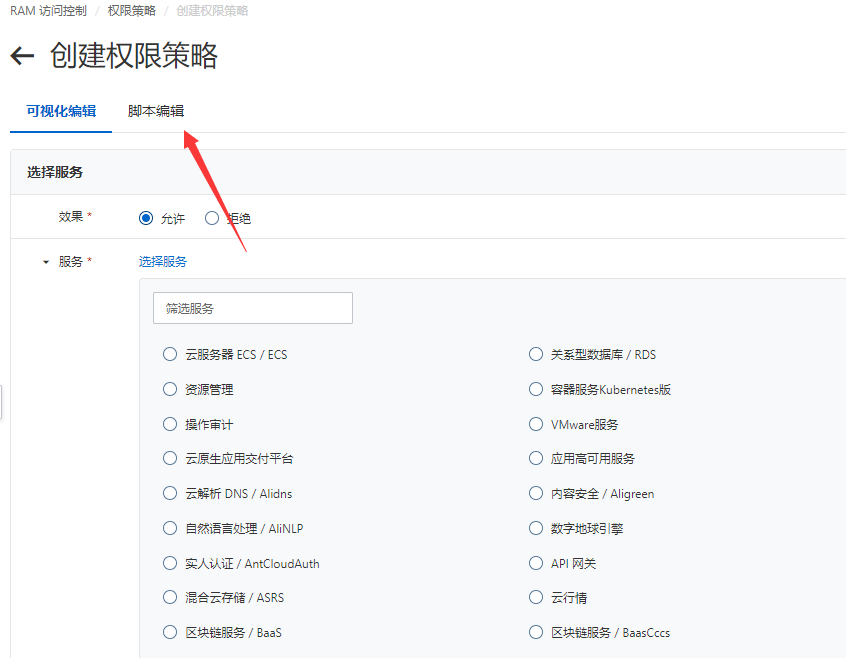
主要是设置Rescource配置对资源的访问 权限
Action:允许的操作
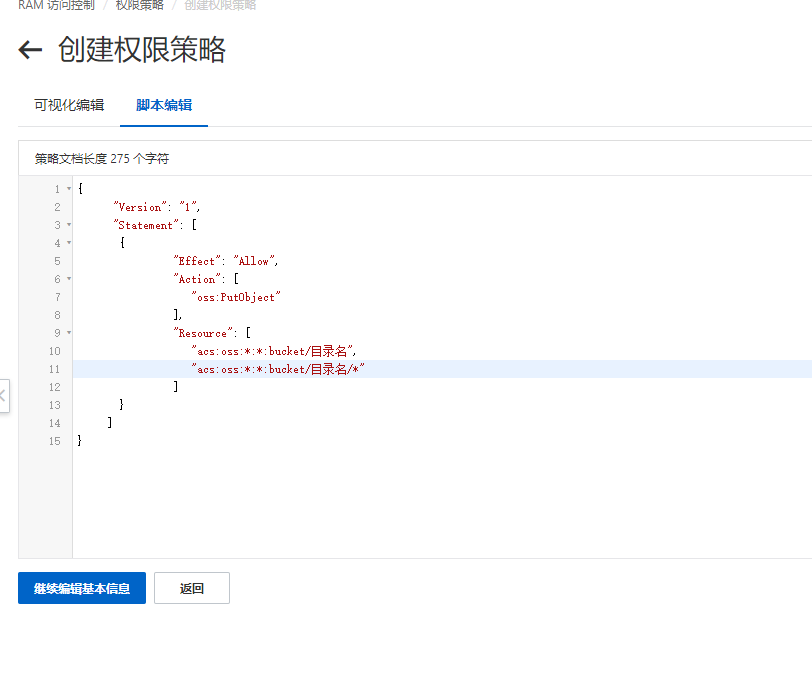
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "oss:PutObject" ], "Resource": [ "acs:oss:*:*:oss的bucket名字/目录", "acs:oss:*:*:oss的bucket名字/目录/*" ] } ]}
如果不限制目录可以这样写
"Resource": [ "acs:oss:*:*:oss的bucket名字", "acs:oss:*:*:oss的bucket名字/*" ]
脚本编辑完成后取个名字保存备用
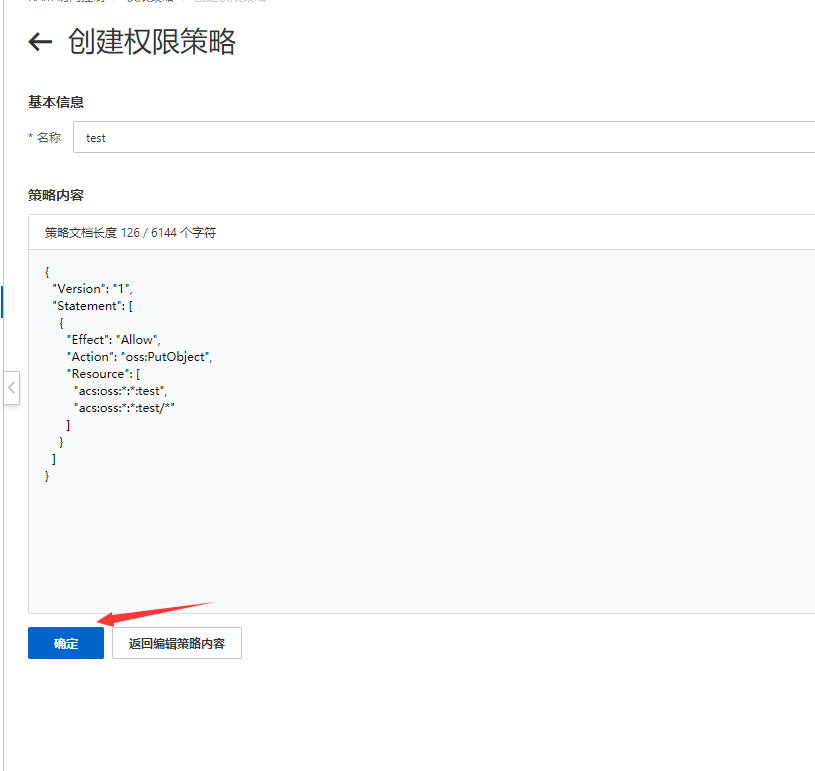
4:为角色添加策略
把上面的脚本权限添加给校色,回到角色列表找到对应的用户选择添加权限
通过名字查找上面添加的策略,然后保存就完成了整个权限的添加。

万事俱备接下来是关于Go语言相关的事情。
6:Go代码上传案例
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"time"
"strconv"
"net/http"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/pem"
"encoding/json"
"crypto"
"crypto/md5"
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/x509"
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha1"
"errors"
"hash"
)
// 请填写您的AccessKeyId。
var accessKeyId string = "<yourAccessKeyId>"
// 请填写您的AccessKeySecret。
var accessKeySecret string = "<yourAccessKeySecret>"
// host的格式为 bucketname.endpoint ,请替换为您的真实信息。
var host string = "http://bucket-name.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"
// callbackUrl为 上传回调服务器的URL,请将下面的IP和Port配置为您自己的真实信息。
var callbackUrl string = "http://88.88.88.88:8888";
// 用户上传文件时指定的前缀。
var upload_dir string = "user-dir-prefix/"
var expire_time int64 = 30
const (
base64Table = "123QRSTUabcdVWXYZHijKLAWDCABDstEFGuvwxyzGHIJklmnopqr234560178912"
)
var coder = base64.NewEncoding(base64Table)
func base64Encode(src []byte) []byte {
return []byte(coder.EncodeToString(src))
}
func get_gmt_iso8601(expire_end int64) string {
var tokenExpire = time.Unix(expire_end, 0).UTC().Format("2006-01-02T15:04:05Z")
return tokenExpire
}
type ConfigStruct struct{
Expiration string `json:"expiration"`
Conditions [][]string `json:"conditions"`
}
type PolicyToken struct{
AccessKeyId string `json:"accessid"`
Host string `json:"host"`
Expire int64 `json:"expire"`
Signature string `json:"signature"`
Policy string `json:"policy"`
Directory string `json:"dir"`
Callback string `json:"callback"`
}
type CallbackParam struct{
CallbackUrl string `json:"callbackUrl"`
CallbackBody string `json:"callbackBody"`
CallbackBodyType string `json:"callbackBodyType"`
}
func get_policy_token() string {
now := time.Now().Unix()
expire_end := now + expire_time
var tokenExpire = get_gmt_iso8601(expire_end)
//create post policy json
var config ConfigStruct
config.Expiration = tokenExpire
var condition []string
condition = append(condition, "starts-with")
condition = append(condition, "$key")
condition = append(condition, upload_dir)
config.Conditions = append(config.Conditions, condition)
//calucate signature
result,err:=json.Marshal(config)
debyte := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(result)
h := hmac.New(func() hash.Hash { return sha1.New() }, []byte(accessKeySecret))
io.WriteString(h, debyte)
signedStr := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
var callbackParam CallbackParam
callbackParam.CallbackUrl = callbackUrl
callbackParam.CallbackBody = "filename=${object}&size=${size}&mimeType=${mimeType}&height=${imageInfo.height}&width=${imageInfo.width}"
callbackParam.CallbackBodyType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
callback_str,err:=json.Marshal(callbackParam)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("callback json err:", err)
}
callbackBase64 := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(callback_str)
var policyToken PolicyToken
policyToken.AccessKeyId = accessKeyId
policyToken.Host = host
policyToken.Expire = expire_end
policyToken.Signature = string(signedStr)
policyToken.Directory = upload_dir
policyToken.Policy = string(debyte)
policyToken.Callback = string(callbackBase64)
response,err:=json.Marshal(policyToken)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("json err:", err)
}
return string(response)
}
func main() {
strIPPort := ":8080";
if (len(os.Args)==3) {
strIPPort = fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", os.Args[1], os.Args[2])
} else if (len(os.Args)!=1) {
fmt.Println("Usage : go run callbackserver.go ")
fmt.Println("Usage : go run callbackserver.go ip port ")
fmt.Println("Example : go run callbackserver.go 11.22.33.44 80 ")
fmt.Println("Example : go run callbackserver.go 0.0.0.0 8080 ")
fmt.Println("")
os.Exit(0)
}
fmt.Printf("\ncallbackserver is running on %s \n", strIPPort);
http.HandleFunc("/", handlerRequest)
err := http.ListenAndServe(strIPPort, nil)
if (err != nil) {
strError := fmt.Sprintf("http.ListenAndServe failed : %s \n", err.Error())
panic(strError)
}
}
func handlerRequest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if (r.Method == "GET") {
response := get_policy_token()
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "POST")
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*")
io.WriteString(w, response)
}
if (r.Method == "POST") {
fmt.Println("\nHandle Post Request ... ")
// Get PublicKey bytes
bytePublicKey, err := getPublicKey(r)
if (err != nil) {
responseFailed(w)
return
}
// Get Authorization bytes : decode from Base64String
byteAuthorization, err := getAuthorization(r)
if (err != nil) {
responseFailed(w)
return
}
// Get MD5 bytes from Newly Constructed Authrization String.
byteMD5, err := getMD5FromNewAuthString(r)
if (err != nil) {
responseFailed(w)
return
}
// verifySignature and response to client
if (verifySignature(bytePublicKey, byteMD5, byteAuthorization)) {
// do something you want accoding to callback_body ...
responseSuccess(w) // response OK : 200
} else {
responseFailed(w) // response FAILED : 400
}
}
}
// getPublicKey : Get PublicKey bytes from Request.URL
func getPublicKey(r *http.Request) ([]byte, error) {
var bytePublicKey []byte
// get PublicKey URL
publicKeyURLBase64 := r.Header.Get("x-oss-pub-key-url")
if (publicKeyURLBase64 == "") {
fmt.Println("GetPublicKey from Request header failed : No x-oss-pub-key-url field. ")
return bytePublicKey, errors.New("no x-oss-pub-key-url field in Request header ")
}
publicKeyURL, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(publicKeyURLBase64)
// fmt.Printf("publicKeyURL={%s}\n", publicKeyURL)
// get PublicKey Content from URL
responsePublicKeyURL, err := http.Get(string(publicKeyURL))
if (err != nil) {
fmt.Printf("Get PublicKey Content from URL failed : %s \n", err.Error())
return bytePublicKey, err
}
bytePublicKey, err = ioutil.ReadAll(responsePublicKeyURL.Body)
if (err != nil) {
fmt.Printf("Read PublicKey Content from URL failed : %s \n", err.Error())
return bytePublicKey, err
}
defer responsePublicKeyURL.Body.Close()
// fmt.Printf("publicKey={%s}\n", bytePublicKey)
return bytePublicKey, nil
}
// getAuthorization : decode from Base64String
func getAuthorization(r *http.Request) ([]byte, error) {
var byteAuthorization []byte
// Get Authorization bytes : decode from Base64String
strAuthorizationBase64 := r.Header.Get("authorization")
if (strAuthorizationBase64 == "") {
fmt.Println("Failed to get authorization field from request header. ")
return byteAuthorization, errors.New("no authorization field in Request header")
}
byteAuthorization, _ = base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(strAuthorizationBase64)
return byteAuthorization, nil
}
// getMD5FromNewAuthString : Get MD5 bytes from Newly Constructed Authrization String.
func getMD5FromNewAuthString(r *http.Request) ([]byte, error) {
var byteMD5 []byte
// Construct the New Auth String from URI+Query+Body
bodyContent, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
r.Body.Close()
if (err != nil) {
fmt.Printf("Read Request Body failed : %s \n", err.Error())
return byteMD5, err
}
strCallbackBody := string(bodyContent)
// fmt.Printf("r.URL.RawPath={%s}, r.URL.Query()={%s}, strCallbackBody={%s}\n", r.URL.RawPath, r.URL.Query(), strCallbackBody)
strURLPathDecode, errUnescape := unescapePath(r.URL.Path, encodePathSegment) //url.PathUnescape(r.URL.Path) for Golang v1.8.2+
if (errUnescape != nil) {
fmt.Printf("url.PathUnescape failed : URL.Path=%s, error=%s \n", r.URL.Path, err.Error())
return byteMD5, errUnescape
}
// Generate New Auth String prepare for MD5
strAuth := ""
if (r.URL.RawQuery == "") {
strAuth = fmt.Sprintf("%s\n%s", strURLPathDecode, strCallbackBody)
} else {
strAuth = fmt.Sprintf("%s?%s\n%s", strURLPathDecode, r.URL.RawQuery, strCallbackBody)
}
// fmt.Printf("NewlyConstructedAuthString={%s}\n", strAuth)
// Generate MD5 from the New Auth String
md5Ctx := md5.New()
md5Ctx.Write([]byte(strAuth))
byteMD5 = md5Ctx.Sum(nil)
return byteMD5, nil
}
/* VerifySignature
* VerifySignature需要三个重要的数据信息来进行签名验证: 1>获取公钥PublicKey; 2>生成新的MD5鉴权串; 3>解码Request携带的鉴权串;
* 1>获取公钥PublicKey : 从RequestHeader的"x-oss-pub-key-url"字段中获取 URL, 读取URL链接的包含的公钥内容, 进行解码解析, 将其作为rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15的入参。
* 2>生成新的MD5鉴权串 : 把Request中的url中的path部分进行urldecode, 加上url的query部分, 再加上body, 组合之后进行MD5编码, 得到MD5鉴权字节串。
* 3>解码Request携带的鉴权串 : 获取RequestHeader的"authorization"字段, 对其进行Base64解码,作为签名验证的鉴权对比串。
* rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15进行签名验证,返回验证结果。
* */
func verifySignature(bytePublicKey []byte, byteMd5 []byte, authorization []byte) bool {
pubBlock, _ := pem.Decode(bytePublicKey)
if (pubBlock == nil) {
fmt.Printf("Failed to parse PEM block containing the public key")
return false
}
pubInterface, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(pubBlock.Bytes)
if (pubInterface == nil) || (err != nil) {
fmt.Printf("x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(publicKey) failed : %s \n", err.Error())
return false
}
pub := pubInterface.(*rsa.PublicKey)
errorVerifyPKCS1v15 := rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15(pub, crypto.MD5, byteMd5, authorization)
if (errorVerifyPKCS1v15 != nil) {
fmt.Printf("\nSignature Verification is Failed : %s \n", errorVerifyPKCS1v15.Error())
//printByteArray(byteMd5, "AuthMd5(fromNewAuthString)")
//printByteArray(bytePublicKey, "PublicKeyBase64")
//printByteArray(authorization, "AuthorizationFromRequest")
return false
}
fmt.Printf("\nSignature Verification is Successful. \n")
return true
}
// responseSuccess : Response 200 to client
func responseSuccess(w http.ResponseWriter) {
strResponseBody := "{\"Status\":\"OK\"}"
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.Header().Set("Content-Length", strconv.Itoa(len(strResponseBody)))
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Write([]byte(strResponseBody))
fmt.Printf("\nPost Response : 200 OK . \n")
}
// responseFailed : Response 400 to client
func responseFailed(w http.ResponseWriter) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
fmt.Printf("\nPost Response : 400 BAD . \n")
}
func printByteArray(byteArrary []byte , arrName string) {
fmt.Printf("++++++++ printByteArray : ArrayName=%s, ArrayLength=%d \n", arrName, len(byteArrary))
for i:=0; i<len(byteArrary); i++ {
fmt.Printf("%02x", byteArrary[i]);
}
fmt.Printf("\n-------- printByteArray : End . \n")
}
type EscapeError string
func (e EscapeError) Error() string {
return "invalid URL escape " + strconv.Quote(string(e))
}
type InvalidHostError string
func (e InvalidHostError) Error() string {
return "invalid character " + strconv.Quote(string(e)) + " in host name"
}
type encoding int
const (
encodePath encoding = 1 + iota
encodePathSegment
encodeHost
encodeZone
encodeUserPassword
encodeQueryComponent
encodeFragment
)
// unescapePath : unescapes a string; the mode specifies, which section of the URL string is being unescaped.
func unescapePath(s string, mode encoding) (string, error) {
// Count %, check that they're well-formed.
mode = encodePathSegment
n := 0
hasPlus := false
for i := 0; i < len(s); {
switch s[i] {
case '%':
n++
if i+2 >= len(s) || !ishex(s[i+1]) || !ishex(s[i+2]) {
s = s[i:]
if len(s) > 3 {
s = s[:3]
}
return "", EscapeError(s)
}
// Per https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3986#page-21
// in the host component %-encoding can only be used
// for non-ASCII bytes.
// But https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6874#section-2
// introduces %25 being allowed to escape a percent sign
// in IPv6 scoped-address literals. Yay.
if mode == encodeHost && unhex(s[i+1]) < 8 && s[i:i+3] != "%25" {
return "", EscapeError(s[i : i+3])
}
if mode == encodeZone {
// RFC 6874 says basically "anything goes" for zone identifiers
// and that even non-ASCII can be redundantly escaped,
// but it seems prudent to restrict %-escaped bytes here to those
// that are valid host name bytes in their unescaped form.
// That is, you can use escaping in the zone identifier but not
// to introduce bytes you couldn't just write directly.
// But Windows puts spaces here! Yay.
v := unhex(s[i+1])<<4 | unhex(s[i+2])
if s[i:i+3] != "%25" && v != ' ' && shouldEscape(v, encodeHost) {
return "", EscapeError(s[i : i+3])
}
}
i += 3
case '+':
hasPlus = mode == encodeQueryComponent
i++
default:
if (mode == encodeHost || mode == encodeZone) && s[i] < 0x80 && shouldEscape(s[i], mode) {
return "", InvalidHostError(s[i : i+1])
}
i++
}
}
if n == 0 && !hasPlus {
return s, nil
}
t := make([]byte, len(s)-2*n)
j := 0
for i := 0; i < len(s); {
switch s[i] {
case '%':
t[j] = unhex(s[i+1])<<4 | unhex(s[i+2])
j++
i += 3
case '+':
if mode == encodeQueryComponent {
t[j] = ' '
} else {
t[j] = '+'
}
j++
i++
default:
t[j] = s[i]
j++
i++
}
}
return string(t), nil
}
// Please be informed that for now shouldEscape does not check all
// reserved characters correctly. See golang.org/issue/5684.
func shouldEscape(c byte, mode encoding) bool {
// §2.3 Unreserved characters (alphanum)
if 'A' <= c && c <= 'Z' || 'a' <= c && c <= 'z' || '0' <= c && c <= '9' {
return false
}
if mode == encodeHost || mode == encodeZone {
// §3.2.2 Host allows
// sub-delims = "!" / "$" / "&" / "'" / "(" / ")" / "*" / "+" / "," / ";" / "="
// as part of reg-name.
// We add : because we include :port as part of host.
// We add [ ] because we include [ipv6]:port as part of host.
// We add < > because they're the only characters left that
// we could possibly allow, and Parse will reject them if we
// escape them (because hosts can't use %-encoding for
// ASCII bytes).
switch c {
case '!', '$', '&', '\'', '(', ')', '*', '+', ',', ';', '=', ':', '[', ']', '<', '>', '"':
return false
}
}
switch c {
case '-', '_', '.', '~': // §2.3 Unreserved characters (mark)
return false
case '$', '&', '+', ',', '/', ':', ';', '=', '?', '@': // §2.2 Reserved characters (reserved)
// Different sections of the URL allow a few of
// the reserved characters to appear unescaped.
switch mode {
case encodePath: // §3.3
// The RFC allows : @ & = + $ but saves / ; , for assigning
// meaning to individual path segments. This package
// only manipulates the path as a whole, so we allow those
// last three as well. That leaves only ? to escape.
return c == '?'
case encodePathSegment: // §3.3
// The RFC allows : @ & = + $ but saves / ; , for assigning
// meaning to individual path segments.
return c == '/' || c == ';' || c == ',' || c == '?'
case encodeUserPassword: // §3.2.1
// The RFC allows ';', ':', '&', '=', '+', '$', and ',' in
// userinfo, so we must escape only '@', '/', and '?'.
// The parsing of userinfo treats ':' as special so we must escape
// that too.
return c == '@' || c == '/' || c == '?' || c == ':'
case encodeQueryComponent: // §3.4
// The RFC reserves (so we must escape) everything.
return true
case encodeFragment: // §4.1
// The RFC text is silent but the grammar allows
// everything, so escape nothing.
return false
}
}
// Everything else must be escaped.
return true
}
func ishex(c byte) bool {
switch {
case '0' <= c && c <= '9':
return true
case 'a' <= c && c <= 'f':
return true
case 'A' <= c && c <= 'F':
return true
}
return false
}
func unhex(c byte) byte {
switch {
case '0' <= c && c <= '9':
return c - '0'
case 'a' <= c && c <= 'f':
return c - 'a' + 10
case 'A' <= c && c <= 'F':
return c - 'A' + 10
}
return 0
}